What Is Hot-Dip Galvanizing?
-
 2022-09-12
2022-09-12
-
Hot-dipped Galvanizing Features:
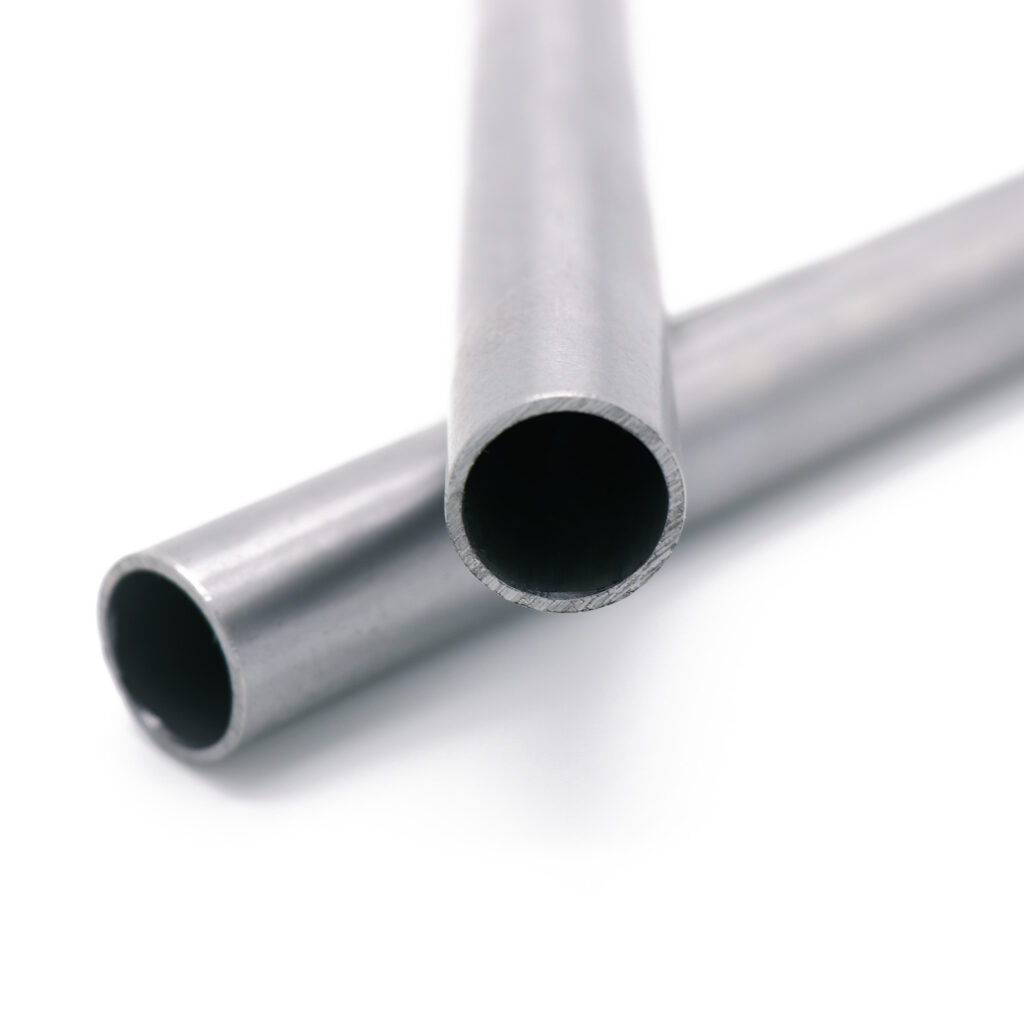

Hot-dipped galvanizing has the advantages of uniform coating and long service life. All our products undergo rigorous quality testing before packing.
Hot-dip galvanizing is the most common method of protecting steel from corrosion. The surface of the steel is dipped in molten zinc and then allowed to cool and solidify on the surface, forming a zinc coating that completely coats the steel and prevents it from further oxidizing.
Our hot-dipped galvanized products are produced with a protective zinc coating, which provides protection against corrosion by acting as a barrier between the metal and its environment.
We have been using it for over 100 years because it’s one of the most effective ways to protect steel from corrosion. Hot-dipped galvanizing provides excellent protection against rusting because it forms an extremely hard layer of zinc oxide (ZnO) or zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) on the surface of the steel. This layer is impenetrable by oxygen or water vapour, so it prevents any further rusting from occurring beneath it.
Hot-dip galvanized products come in many shapes and sizes including angle iron, channels/tubes/pipes/cheeks.
The thickness of the galvanized coating is 0.3mm-0.8mm, and the colour is black.
The surface of hot-dipped galvanizing is smooth, bright, and beautiful. You can use it as a decorative material in architecture and exterior decoration.
Our Products Include:
1)Galvanized steel wire mesh
2)Galvanized wire mesh fabrics
3)Galvanized steel barbed wire fence panels
Advantages Of Hot-dip Galvanizing:
1: Lower Costs
Hot-dip galvanizing is more cost-effective than other coating methods. It is this reason why it is the most widely popular method of galvanizing in the world today.
2: Extremely Long Life
More importantly, the process of hot-dip galvanizing results in a very tough, durable, and corrosion-resistant coating that is able to withstand extreme conditions such as high temperatures, humidity, saltwater, and even sandblasting.
3: Requires less maintenance
The coating of hot-dip galvanizing provides all the protection that your metal product needs without any need for maintenance or repair work at all! This saves you money on labour costs and ensures that your product will always be ready for use whenever you need it!
4: Reliability
Hot-dip galvanizing produces a very reliable coating that will never let you down when needed most! The process also produces an extremely strong bond between the base metal and the protective coating itself so that there are no chances of rusting or corrosion taking place underneath the paintwork at all!
5: Tougher Coating
Hot-dip galvanizing produces an extremely tough protective layer.
FAQ:
- How long does hot-dipped galvanizing last?
The lifespan of hot-dipped galvanized steel is between 15 and 25 years.
- What are the drawbacks of hot dip galvanizing?
There are two main drawbacks of hot dip galvanizing:
Firstly, it requires high temperatures to work effectively. This can cause problems in cold climates where condensation may form on the surface of the steel which will affect its performance and appearance.
Second, because it requires high heat, it may discolour nearby objects — especially if they consist of wood or other organic materials.
- Can you paint it?
No. The best way to protect your hot-dip galvanized steel is by painting it after installation. However, it’s important to note that painting over hot-dipped galvanized steel can cause discolouration in the paint due to chemical reactions between the paints and the zinc coating on your metal items. And this means that if you want your paint job to look good forever then painting over hot dipped galvanized steel isn’t an option for you!
- Can you Galvanise over galvanized?
Yes! You can build up layers of protection on top of your current layer.
Hot-Dip Galvanizing Application:
Hot-dip galvanizing is an electrochemical process used to protect steel from corrosion. It consists of immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc and then passing an electric current through it to produce zinc ions. The zinc ions form a dense, even, corrosion-resistant layer of zinc oxide on the surface of the metal. This layer provides protection against corrosion by blocking oxygen from reaching the unprotected steel underneath it.
Hot-dip galvanizing is most commonly used on steel structures such as bridges, towers, and poles. It is also used on railway tracks, power lines, and other transportation infrastructure that cannot be easily disassembled. What’s more, the process can also be used on aluminium alloys if they are coated with nickel before being dipped into the zinc bath.
Because hot-dip galvanizing produces a thick coating of zinc oxide, it is not suitable for thin items like wires or tubing that are already corroding due to their thin walls. It also cannot appear on surfaces that need to be electrically conductive (such as electrical contacts), as it will create insulating layers between these surfaces and their contacts/cables/wires etc).
How Do You Test Hot-dip Galvanized?
Two different methods can measure the coating thickness of hot-dip galvanized steel; a magnetic thickness gauge and optical microscopy. Utilizing a magnetic thickness gauge is a non-destructive, simple way to measure coating thickness.
Magnetic Thickness Gauges
Magnetic thickness gauges use the eddy current principle. They operate by passing an alternating current through a coil within the gauge, which produces an oscillating magnetic field around the coil. As the alternating current passes through the metal being checked, it induces eddy currents in that metal. These eddy currents produce magnetic fields of their own that oppose the original oscillating magnetic field. As they do so, they create an electromagnetic force which to detect with sensors within the gauge.
This force is proportional to the thickness of the metal being tested and thus gives an accurate reading of coating thickness over wide ranges of coating thicknesses (typically 0 – 2mm). The gauge will usually register this number digitally for easy reading.
Optical Microscopy
It is another method to measure coating thickness but requires more preparation time than electromagnetic measurement does. In order to conduct optical microscopy testing properly, it is necessary that you have access to a high-resolution microscope with good magnification capabilities.
Hot-dip Galvanized Has Those Models:
Product Name: EN 10305 Galvanized Hydraulic Seamless Steel Tube
Standard: EN10305-4 (DIN2445/2), EN10305-1 (DIN2391), ASTM A179
Steel grade: E235 (ST35 ST37.4), E355 (ST52 ST52.4)
Size: OD: 4-120mm
WT: 0.5-10mm
Length: fixed 6m or as your request
Finish: Galvanized — This tube has a zinc coating of 8 to 12μm
Delivery condition: +N (NBK) normalized under a controlled atmosphere
Delivery time: 15-45 days, according to the quantity you need and the item in stock
Shape: round
Process: perforation/pickling/phosphating/cold drawn/cold rolling/annealing/anaerobic annealing
Protection: Anti-rust oil on the inner and outer surfaces, plastic covers at both ends.
Conclusion:
If you have any questions about Precision Seamless Hydraulic Steel Tube product quality, usage, etc., please contact us: Global Steeltube.